The curated resources linked below are an initial sample of the resources coming from a collaborative and rigorous review process with the EAD Content Curation Task Force.
 Reset All
Reset All
This lesson is designed to help students develop the skills and understanding to engage in civic dialogue across differences. Students will practice empathy through telling each other’s stories.

The Roadmap
Mikva Challenge


Students will examine Alabama’s past practice of convict leasing, discussing the parties in favor of and against the work process, and they will analyze a persuasive pamphlet urging the end of convict leasing.

The Roadmap



Alabama Department of Archives and History

In this lesson, students will think about the definition of democracy and then consider how it might relate to the communities and culture in which they live and participate.

The Roadmap


Facing History and Ourselves


FIRE's First Amendment Curriculum guides students in learning why their free speech rights are so valuable, how they are essential to learning and to democracy, and about their proven history in securing justice and fairness for disempowered and marginalized populations. Centered in social and emotional learning, these lessons demonstrate how basic rights can be threatened and illustrate ways to protect them.

The Roadmap


Foundation for Individual Rights in Education (FIRE)


The Coronavirus Pandemic of 2020 has increased public awareness of the field of public health, which takes as its key goals “protecting and improving the health of people and their communities”(according to the CDC). In part because public health is so little understood or discussed in the U.S., government interventions to respond to the pandemic, including efforts to encourage masking and vaccinations, met with significant controversy and a wide variety of responses on the state and local levels. But the notion of government response to public health crises was not new in 2020; indeed, American public health measures including quarantine and inoculation predate the founding of the United States.
This Spotlight Kit covers a range of historic events in the realm of public health, including (but not limited to) Yellow Fever in 1793, public health crises of the Civil War, the 1918 flu epidemic, and the development of the polio vaccine in 1955. The documents herein reveal perennial questions about what the responsibility of the government is to its citizens’ health and what the limitations are to the public will for government intervention.
The resources in this spotlight kit are intended for classroom use, and are shared here under a CC-BY-SA license. Teachers, please review the copyright and fair use guidelines.



The Roadmap

















- Primary Resources by Era/DateEighteenth Century (4)Nineteenth Century (5)Early Twentieth Century (including 1918 Flu Pandemic) (4)Later Twentieth Century (5)
- All 18 Primary ResourcesFrom George Washington to William Shippen, Jr. (1777)
During the Revolutionary War, according to military historians, approximately 90% of deaths among soldiers were the result of the spread of smallpox. As a result, Washington decided to mandate the vaccination of the troops – a process more dangerous and complicated in that era than our public vaccination campaigns today.
CitePrintShare“From George Washington to William Shippen, Jr., 6 February 1777,” Founders Online, National Archives, https://founders.archives.gov/documents/Washington/03-08-02-0281. [Original source: The Papers of George Washington, Revolutionary War Series, vol. 8, 6 January 1777 – 27 March 1777, ed. Frank E. Grizzard, Jr. Charlottesville: University Press of Virginia, 1998, p. 264.]
Thomas Jefferson to James Madison (1793)TranscriptThomas Jefferson to James Madison, 1793: “I think there is rational danger, but that I had before announced that I should not go till the beginning of October, & I do not like to exhibit the appearance of panic. Besides that I think there might serious ills proceed from there being not a single member of the administration in place. Poor Hutcheson dined with me on Friday was sennight, was taken that night on his return home, & died the day before yesterday.”
In this letter, Thomas Jefferson describes how the yellow fever is harming countless people, even those in the government, yet no one seems to know what can be done. Alexander Hamilton is ill, others are sick or dying, and Jefferson writes about avoiding the appearance of “panic” for the public.
1The resources in this spotlight kit are intended for classroom use. Teachers, if your use will be beyond a single classroom, please review the copyright and fair use guidelines.CitePrintShareThomas Jefferson to James Madison, September 8, with Fragment Copy. -09-08, 1793. Manuscript/Mixed Material. Retrieved from the Library of Congress, accessed from the Library of Congress on March 27, 2022, at www.loc.gov/item/mtjbib007979/.
Note: If you select to download the PDF below the image, you can see a transcript of the letter.
A Narrative of the Proceedings of the Black People, during the Late Awful Calamity in Philadelphia, in the Year 1793TranscriptA narrative of the proceedings of the black people, during the late awful calamity in Philadelphia, in the year 1793:
“We feel ourselves sensibly aggrieved by the censorious epithets of many, who did not render the least assistance in the time of necessity, yet are liberal of their censure of us, for the prices paid for our services, when no one knew how to make a proposal to any one they wanted to assist them. At first we made no charge but left it to those we served in removing their dead, to give what they thought fit–we set no price, until the reward was fixed by those we had served. After paying the people we had to assist us, our compensation is much less than many will believe.” (pp. 7-8)
This primary source reflects the incredible help that African Americans provided during Philadelphia’s yellow fever epidemic of 1793. Those who helped recount speaking with the mayor about what could be done and working with the government of the city in order to help those in need. Later in the document, the writers recount that they asked for pay for their many services given during this time of illness and need, yet some citizens turned against them.
CitePrintShareJones, Absalom, et al. A narrative of the proceedings of the black people, during the late awful calamity in Philadelphia, in the year: and a refutation of some censures thrown upon them in some late publications. Philadelphia: Printed for the authors, by William W. Woodward, 1794. Pdf. Accessed March 27, 2022 from the Library of Congress at www.loc.gov/item/02013737/
Note: This is a 32 page primary source document in its original form. If you wish to access a transcript of portions of this document in Microsoft Word form, that can be accessed from the Texas State University Library Guides; the citation for this is as follows:
Absolom Jones and Richard Allen, “On Black Philadelphians’ Conduct During the Yellow Fever Epidemic of 1793-1794,” ExplorePAhistory.com, accessed March 27, 2022 fro the Texas State University Library Guides at https://explorepahistory.com/odocument.php?docId=1-4-169.
“Account of the yellow fever outbreak in Philadelphia, October 11-14, 1793” (1793)“Account of the yellow fever outbreak in Philadelphia, October 11-14, 1793”TranscriptPhiladelphia 11th october 1793 11 OClock A.M. “The fever from all that I can learn is more fatal than ever, yesterday a vast number of burials – I do not expect any abatement of the fever before we have rain and high winds – The day before yesterday we were witness to what appears to me Shocking – a Coffin was brought to the entrance of Welsh’s alley, where it stayed sometime for the man to die before he was put into the Coffin, Such hurry must bury many alive.”
New York 14th October 1793 ½ past 10 OClock A.M. “The mail is arrived, I have no letters but I have seen Several, The malady in Philada continues dreadful, one hundred and thirty Seven were buried on friday last by the Committee independent of many who were buried by their friends, Fifty eight were Carried from Bush hill to Pottersfield Thursday last.—”
The federal government left Philadelphia in 1793 to avoid the yellow fever epidemic; the federal government’s response to the health concern was to leave the city. This letter is from Secretary of War Henry Knox and relates to the government weighing whether or not it was safe for them to go back to Philadelphia (students may need to be reminded that before Washington, DC, the federal government met in Philadelphia).
CitePrintShare“Account of the yellow fever outbreak in Philadelphia, October 11-14, 1793”, from the Gilder Lehrman Collection. Accessed on March 27, 2022 from https://www.gilderlehrman.org/history-resources/spotlight-primary-source/reports-yellow-fever-epidemic-1793
Note: A transcript of this letter is also available from this same page cited above.
The Shattuck Report (1850)Known as the Shattuck Report and done with the Massachusetts Sanitary Commission in 1850, this was the first in-depth look at public health. It focused on health and living conditions in Boston but had far-reaching impacts in bringing public health to the forefront of important national issues. According to many, this was the first attempt to get a public health code in place in a major American city. Shattuck’s report came at a time when the government was doing little to help immigrants arriving to the US, low-wage workers were living in unsanitary conditions, the working poor received almost no government help, and healthcare was nearly nonexistent for those living in poverty. The report revealed the need for public health codes and government intervention; according to LSU Biotech Law, “This report is one of the fundamental documents in public health in the United States. It is the first systematic use of birth and death records and other demographic data to describe the health of a population. Its recommendations became the foundation of the sanitation movement in the United States. . . “ This report also outlines technology as a necessity for government intervention in public health, mentioning everything from sanitation systems to sanitation laws.
CitePrintShareHistoric Public Health Books: “The Shattuck Report: LEMUEL SHATTUCK - REPORT OF A GENERAL PLAN FOR THE PROMOTION OF GENERAL AND PUBLIC HEALTH DEVISED, PREPARED AND RECOMMENDED BY THE COMMISSIONERS APPOINTED UNDER A RESOLVE OF THE LEGISLATURE OF MASSACHUSETTS, RELATING TO A SANITARY SURVEY OF THE STATE. (1850)”; accessed from LSU Biotech Law on March 27, 2022 at https://biotech.law.lsu.edu/cphl/history/books/sr/
Note: This is a transcript of the entire book by Lemuel Shattuck. From this link provided above, you can select to view any page on the original primary source book from 1850.
“Rules for preserving the health of the soldier” (1861)“Rules for preserving the health of the soldier” (1861)Transcript“To secure by all possible means the health and efficiency of our troops now in the field, and to prevent unnecessary disease and suffering. . .. Every officer and soldier should be carefully vaccinated with fresh vaccine matter, unless already marked by small-pox.”
This book outlines health advice for soldiers; it was published by the federal government under the US Sanitary Commission during the Civil War, at a time when the Union Army needed government assistance to keep soldiers healthy. The work also discusses everything from diet to sanitation.
CitePrintShare“Rules for preserving the health of the soldier”, provided by the U.S. National Library of Medicine Digital Collections; accessed March 27, 2022, from https://collections.nlm.nih.gov/bookviewer?PID=nlm:nlmuid-101201682-bk.
If you wish to read a transcript of portions of this work, you can use the following source:
Teach US History.org, “Rules for Preserving the Health of the Soldier”, accessed March 27, 2022 at https://www.teachushistory.org/civil-war/resources/rules-preserving-health-soldier#:~:text=Every%20officer%20and%20soldier%20should,the%20exigencies%20of%20service%20permit.
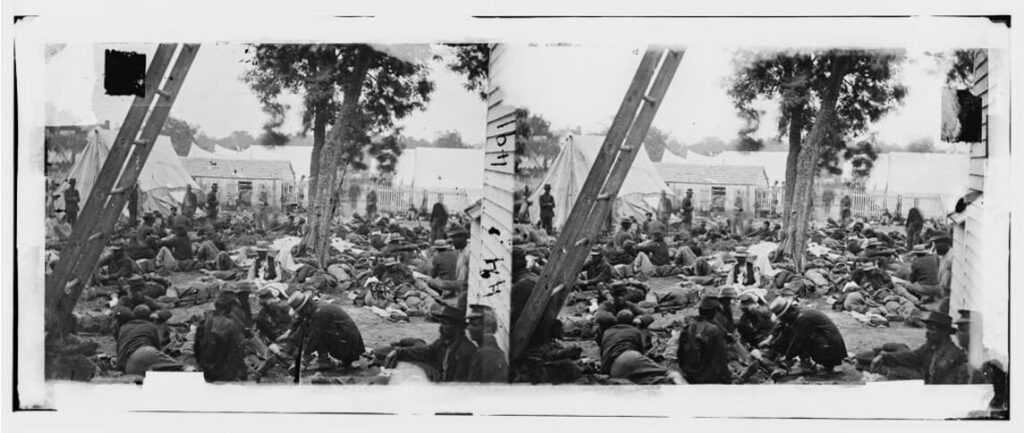
Union field hospital after the battle of June 27 (1862)This photograph shows a Union Civil War hospital in June 1862. This photograph could be used in conjunction with the “Rules for the preserving the health of the soldier” (the primary source listed above) to showcase some of the measures taken for the health of soldiers.
CitePrintShareGibson, James F, photographer. Savage Station, Virginia. Union field hospital after the battle of June 27. June. Photograph. Retrieved from the Library of Congress, www.loc.gov/item/2018671740/.
Letter from Dr. John H. Rapier, Jr. to his uncle (1864)Transcript“I drew $100 less war tax $2.50 for Medical Services rendered the U.S. Government. … I must tell you coloured men in the U.S. Uniform are much respected here, and in visiting the various Departments if the dress is that of an Officer, you receive the military salute from the ground as promptly as if your blood was a Howard or Plantagenent instead of a Pompey or Cuffee’s. … I had decided not to wear the uniform but I have altered my mind—and I shall appear hereafter in full dress gold lace, pointed hat, straps and all. Mr. Fred Douglass spoke here last night to an immense audience and today the President sent for him to visit him in the Capitol.”
This four-page August 19, 1864 letter is from African American surgeon Dr. John H. Rapier, Jr. In the letter, Dr. Rapier recounts being paid by the US government for his medical services. This primary source shows the important role of African American medical practitioners in the Civil War, and makes reference to Frederick Douglass being summoned by the President and meeting with Dr. Rapier thereafter.
CitePrintShareLetter from Dr. John H. Rapier, Jr. to his uncle James P. Thomas, Esq., St. Louis, Missouri, from Freedmen's Hospital, Washington, D.C., August 19, 1864 (transcript available). Courtesy Moorland-Spingarn Research Center, Howard University. Accessed March 27, 2022 from the NIH US National Library of Medicine at https://www.nlm.nih.gov/exhibition/bindingwounds/education/onlineactivities.html
Hygienic Laboratory at the Marine Hospital, Staten Island, New York (1887-1891)These photographs are from the Marine Hospital at Staten Island, New York, where the Hygienic Laboratory was established in 1887. The tents are for people with tuberculosis; Joseph James Kinyoun was the Assistant Surgeon at this location and urged isolation as a way to combat tuberculosis. According to the NIH, this Marine Hospital “marked the beginning of the National Institutes of Health and laid the groundwork for government-supported scientific research in the United States”. A major purpose of this location was to look for diseases among immigrants arriving from Europe, at a time when anti-immigrant beliefs were already a problem in the US.
CitePrintShareNational Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIH), “The Hygienic Laboratory - Abutment”, access from the NIH on March 27, 2022 at https://www.niaid.nih.gov/about/joseph-kinyoun-indispensable-man-hygienic-laboratory
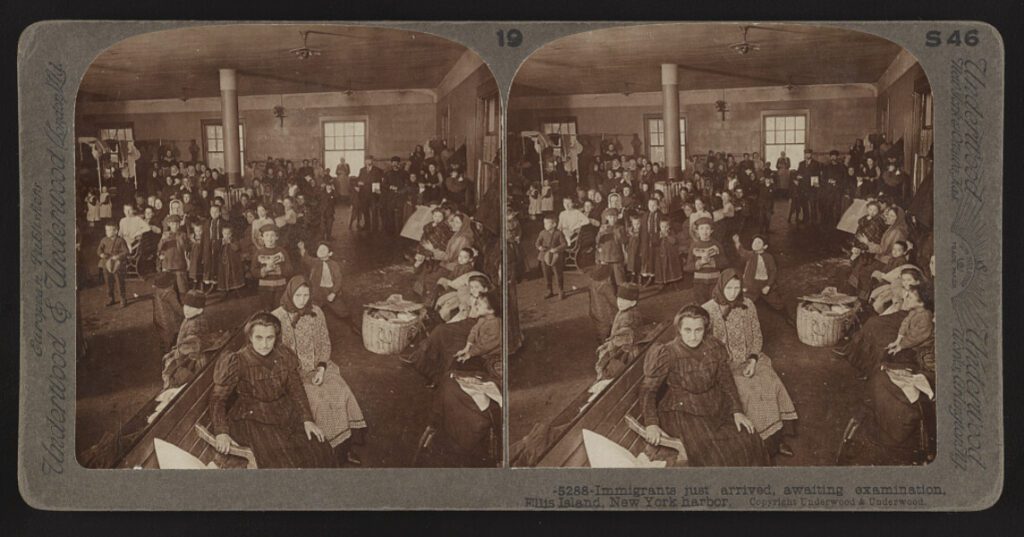
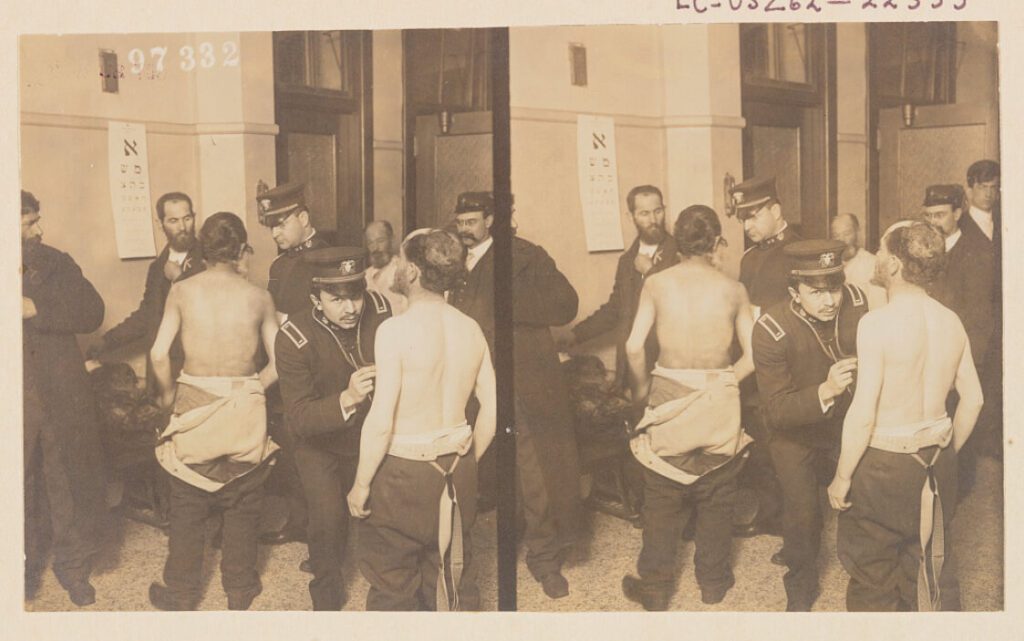
Photographs from Ellis Island (1907)Physicians examining a group of Jewish immigrants (1907)Immigrants just arrived, awaiting examination, Ellis Island, New York harbor (1907)This 1907 photograph shows immigrants being examined at Ellis Island. The US government required medical examinations upon arrival in the US. It could be important to point out public perceptions of immigrants at this time in American history, and how anti-immigrant beliefs were influencing government decisions about medicine and health.
CitePrintShareUnderwood & Underwood, Copyright Claimant. Physicians examining a group of Jewish immigrants. Photograph. Access March 27, 2022 from the Library of Congress at www.loc.gov/item/2012646350/
Underwood & Underwood. Immigrants just arrived, awaiting examination, Ellis Island, New York harbor. [London: underwood & underwood, european publishers, ltd., between 1870 and 1920] Photograph. Accessed March 27, 2022 from the Library of Congress at www.loc.gov/item/2017660810/
Birmingham, Alabama Board of Education School Board Minutes (1918)In terms of government public health initiatives over time, local governments are an important part of that history. This primary source is from Birmingham, Alabama’s School Board minutes from December 1918, in which the possibility of closing schools due to the flu epidemic. The document explains that doctors of the Committee of Health have been consulted on the issue as well. This could be a useful primary source for studying local government decisions in public health issues.
CitePrintShareBirmingham, Alabama Board of Education December 3, 1918 School Board Minutes. Published: Ann Arbor, Michigan: Michigan Publishing, University Library, University of Michigan. Courtesy of: Department of Archives and Manuscripts, Birmingham Public Library, Birmingham, AL. Accessed March 29, 2022 from the Influenza Encyclopedia, from the University of Michigan Center for the History of Medicine and Michigan Publishing, University of Michigan Library Influenza Archive, at
“Swat the Flu…”: The Bismarck Tribune (1919)This 1919 newspaper article has the headline “Swat the Flu is Slogan for 1919 Campaign Against Dread Destroyer that Looms Again: Measure Approved in Both Houses of Congress Would Appropriate $5,000,000 for Investigation of Epidemic Which Swept Over America in 1918, Costing Thousands of Lives”. The article details government actions regarding public health during the 1918-1919 flu epidemic.
CitePrintShareThe Bismarck tribune. [volume] (Bismarck, N.D.), 29 July 1919. Chronicling America: Historic American Newspapers. Lib. of Congress. Accessed March 29, 2022 from the Library of Congress at https://chroniclingamerica.loc.gov/lccn/sn85042243/1919-07-29/ed-1/seq-1/
President Coolidge, Address at the Annual Session of the American Medical Association (1927)This address, given by President Coolidge to the American Medical Association, speaks broadly to the role of the field of public health and the trust he feels society must place in science and medicine.
President Calvin Coolidge, Address at the Annual Session of the American Medical Association, Washington, D.C., May 17, 1927
Ladies and Gentlemen:“...Those who have witnessed the general paralysis which prevails when even a moderate epidemic breaks out can not help but realize that one of the most important factors of our everyday existence is the public health, which has come to be dependent upon sanitation and the medical profession. We are constantly in receipt of the beneficial activities of these efforts in the disposition of waste, the water we drink, the food we eat, and even in the air we breathe. This great work is carried on partly through private initiative, partly through Government effort, partly by a combination of these two working in harmony with the science of chemistry, of engineering, and of applied medicine. In its main aspects it is preventive, but in a very large field it is remedial. Without this service our large centers of population would be overwhelmed and dissipated almost in a day and the modern organization of society would be altogether destroyed. The debt which we owe to the science of medicine is simply beyond computation or comprehension….
If there is any one thing which the progress of science has taught us, it is the necessity of an open mind. Without this attitude very little advance could be made. Truth must always be able to demonstrate itself. But when it has been demonstrated, in whatsoever direction it may lead, it ought to be followed.”
CitePrintShare“Address at the Annual Session of the American Medical Association, Washington, D.C. | The American.” The American Presidency Project, https://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/documents/address-the-annual-session-the-american-medical-association-washington-dc.
The Polio Vaccine Assistance Act of 1955This 1955 primary source is about the US government’s Polio Vaccine Assistance Act and the US government’s public health efforts to fight polio. This two-page document explains how states will receive money for vaccination programs and distribute the vaccine, among other details. Notice the first page calls this a “new advance in preventive medicine”.
CitePrintShareAJPH: A Publication of the American Public Health Association, Otis L. Anderson, MD, F.A.P.H.A, “The Polio Vaccine Assistance Act of 1955”, October 1955. Accessed March 27, 2022 from the AJPH at https://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/pdf/10.2105/AJPH.45.10.1349#:~:text=The%20Polio%20Vaccine%20Assistance%20Act%20of%201955%2C%20passed%20by%20the,of%20planning%20and%20conducting%20vaccination
White House Press Release on the Salk Polio Vaccine (1955)This 1955 White House press release details President Eisenhower’s honoring Jonas Salk with a “citation for his extraordinary achievement” in developing a polio vaccine. Eisenhower, in this press release, details the massive efforts the National Foundation for Infantile Paralysis has taken to work towards a polio vaccine. President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s own struggle with polio, and the gratitude of America as a whole, are also discussed.
CitePrintShareWhite House press release with text of citations given by the President to Dr. Jonas E. Salk and the National Foundation for Infantile Paralysis, April 22, 1955 [DDE's Records as President, Official File, Box 511, 117-I-1 Salk Polio Vaccine (8); NAID #12166355]. Accessed March 29, 2022 from the Dwight D. Eisenhower Presidential Library at https://www.eisenhowerlibrary.gov/sites/default/files/research/online-documents/salk/salk-c.pdf
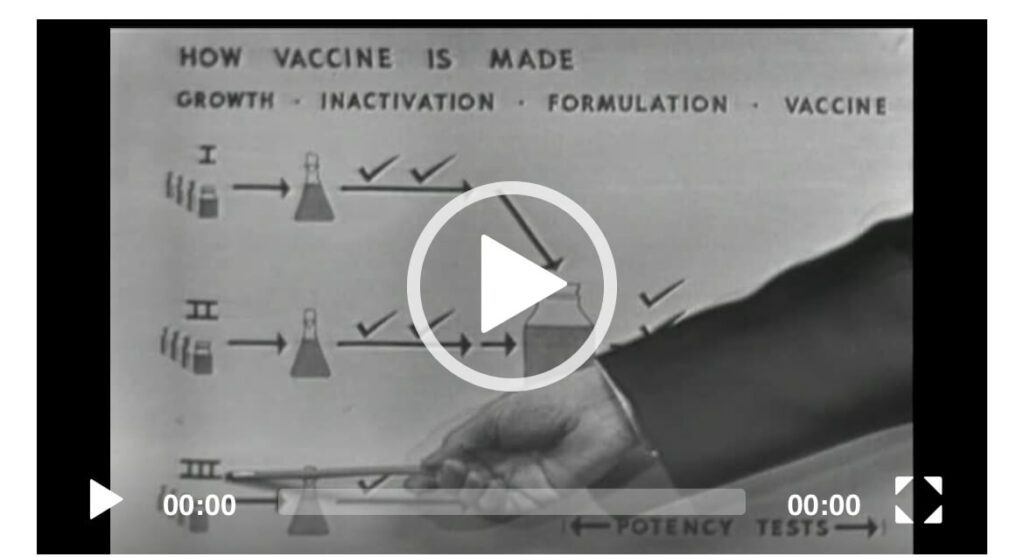
Public Health Video (1955)This Library of Congress 14 minute and 35 second video is from 1955 and details the efforts made to fight polio. From the NBC Television Collection, this primary source allows students to watch a primary source video that details items such as how vaccines are made, including the safety of vaccines. The description reads: “HEW Secretary Oveta Culp Hobby and Surgeon General Leonard Scheele talk about the Salk polio vaccine and assuage concerns about its safety”. (HEW is “Health, Education, and Welfare”.)
CitePrintShareScheele, Leonard Andrew, et al. A Special Report on Polio. 1955. Video. Accessed March 29, 2022 from the Library of Congress at www.loc.gov/item/mbrs00056792/
Special Message to the Congress on the Nation's Health (1964)This address to Congress delineates a public health agenda that includes numerous measures for increasing both the national and international commitments to health infrastructure and access. In doing so, it connects issues of public health and access to health care to President Johnson’s War on Poverty.
President Lyndon B. Johnson, Special Message to the Congress on the Nation's Health (1964)
To the Congress of the United States:The American people are not satisfied with better-than-average health. As a Nation, they want, they need, and they can afford the best of health:
--not just for those of comfortable means.
--but for all our citizens, old and young, rich and poor.
In America,
--There is no need and no room for second-class health services.
...Too many Americans still are cut off by low incomes from adequate health services. Too many older people are still deprived of hope and dignity by prolonged and costly illness. The linkage between ill-health and poverty in America is still all too plain.
In its first session, the 88th Congress made some important advances on the health front:
--It acted to increase our supply of physicians and dentists.
--It began a Nation-wide attack on mental illness and mental retardation.
--And it strengthened our efforts against air pollution.
But our remaining agenda is long, and it will be unfinished until each American enjoys the full benefits of modern medical knowledge.
Part of this agenda concerns a direct attack on that particular companion of poor health--poverty. Above all, we must see to it that all of our children, whatever the economic condition of their parents, can start life with sound minds and bodies.
My message to the Congress on poverty will set forth measures designed to advance us toward this goal.
In today's message, I present the rest of this year's agenda for America's good health.
CitePrintShareJohnson, Lyndon B. “Special Message to the Congress on the Nation's Health.” The American Presidency Project, 10 February 1964, https://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/documents/special-message-the-congress-the-nations-health.
Surgeon General's Report on Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (1987)The Reagan Administration was slow to respond to the initial emergence and spread of AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). Political activism, both within and outside of the LGBTQ community, pushed for more government support, resources, and attention to the disease and its victims. As a National Library of Medicine profile of Surgeon General C. Everett Koop explains, “ In 1986, he was finally authorized to issue a Surgeon General's report on AIDS. In 1988, he mailed a congressionally-mandated information brochure on AIDS to every American household.”
- Everett Koop, Surgeon General's Report on Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (1987):
“Every person can reduce the risk of exposure to the AIDS virus through preventive measures that are simple, straightforward, and effective. However, if people are to follow these recommended measures-to act responsibly to protect themselves and others-they must be informed about them. That is an obvious statement, but not a simple one. Educating people about AIDS has never been easy.
From the start, this disease has evoked highly emotional and often irrational responses. Much of the reaction could be attributed to fear of the many unknowns surrounding a new and very deadly disease. This fear was compounded by personal feelings regarding the groups of people primarily affected-homosexual men and intravenous drug abusers. Rumors and misinformation spread rampantly and became as difficult to combat as the disease itself. It is time to put self-defeating attitudes aside and recognize that we are fighting a disease-not people. We must control the spread of AIDS, and at the same time offer the best we can to care for those who are sick.”
CitePrintShareKoop, CE. “Surgeon General's report on acquired immune deficiency syndrome.” NCBI, 1987, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1477712/.
Education for American Democracy

In this activity, students will use a variety of resources to differentiate between the popular memory of the March and Washington and what actually happened.

The Roadmap



Albert Shanker Institute

In this lesson plan, students explore the connection between literature, imagination, and democracy by engaging with the work of acclaimed author Azar Nafisi, whose work reflects her experiences living and teaching in her native country of Iran, a theocratic state where the government routinely oppressed its citizens, and in the democratic United States, where she later became a citizen.

The Roadmap


Facing History and Ourselves


The Montgomery Bus Boycott is often understood in overly-simplified terms - the result of Rosa Parks refusing to give up her seat. In this lesson, students build a more complex understanding of the causes and context of the boycott as they analyze four historical documents.

The Roadmap


Stanford History Education Group


In this lesson plan, students consider the importance of young people in democracy and analyze stories of civic participation using a framework of questions created by Danielle Allen.

The Roadmap


Facing History and Ourselves


As a highly-structured model for conversation, Deliberations allow teachers to help students cooperatively discuss contested political issues by carefully considering multiple perspectives and searching for consensus. This Deliberation focuses on banning hate speech.

The Roadmap

Street Law Inc.


The Speak Up Speak Out facilitation guide is a project-based learning curriculum. It enables students to work together as teams to identify community problems, conduct research about the problem and its root causes, and craft innovative solutions that allow students to take tangible action.

The Roadmap



Annette Strauss Institute for Civic Life


This lesson will use primary source documents to explore life during the Great Depression.

The Roadmap


Alabama Department of Archives and History